
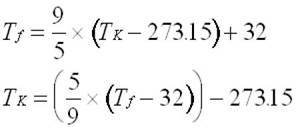
The temperature measurement in Kelvin is used in science. The temperature measurement in Fahrenheit (F) is mainly common in the US, but also in England. A temperature difference of 1K corresponds to a temperature difference of 1 ° C. The movement of particles doesn`t take place there. The Kelvin scale goes back to the English physicist William Thomson, who was ennobled to Lord Kelvin. In contrast to the Kelvin or Fahrenheit scale the zero point is not defined by the water characteristic or a salt mixture, but above the absolute zero point. Only later both values were exchanged resulting in the now common temperature scale in degrees Celsius. The Swedish scientist Anders Celsius defined in 1742 the freezing point of water as 100 ° C and the steam point as 0☌. To convert the temperature TF (☏) to TC (☌): The normal body temperature of 37.7° Celsius is thus at approx. With a freezing mixture of ice, water and ammonia he reached -17.78 ° C (= 0 ° Fahrenheit).įinally, the freezing point and the boiling point of water were defined as fixed points and divided into 180 scale divisions. He determined the lowest temperature he could produce for the zero point.

The Fahrenheit unit for temperature was defined 1714 by the scientist Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit. The temperature is measured according to the International System SI in degrees Celsius (° C) or Kelvin (K). Further to convert Fahrenheit degrees into Kelvins the formula used is, (☏ 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 K. and the basic formula used for Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion is (☏ 32) × 5/9 ☌. At the possibly lowest temperature (absolute zero point) this movement comes to the standstill. The basic formula used to convert Celsius to Kelvin scale is ☌ + 273.15 K. The motion increases with rising temperature. The molecules of a gas, a liquid or a solid body are in constant motion. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a collection of particles or objects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
